Sports nutrition is an essential field for athletes and those who practice physical activities who seek to optimize their performance, accelerate recovery and achieve better results. A balanced diet, rich in nutrients, is the basis for good performance, but, in many cases, supplements and vitamins can be strategic allies to meet the specific needs of each individual.
What are considered Dietary Supplements?
Food supplements are products formulated to complement the diet and provide nutrients that may be in insufficient quantities in the daily diet. These supplements may contain vitamins, minerals, amino acids, fatty acids, proteins, fiber, herbs, plant extracts and other components that are intended to improve health, increase physical performance or correct nutritional deficiencies.

They are available in different forms, such as tablets, capsules, powders, bars or liquids, and are widely used by people with specific nutrient needs or by athletes looking to optimize their performance.
The Role of Supplements in Sports Nutrition
Food supplements are products designed to complement the diet, providing nutrients that may be difficult to obtain in sufficient quantities through food alone.
They can be divided into several categories according to their functions and benefits:
Proteins
Supplements such as whey protein, casein and vegetable protein are popular for promoting muscle recovery, stimulating muscle growth and preventing loss of lean mass. They offer a concentrated source of essential amino acids, fundamental for protein synthesis in the body.
Amino acids
BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids) and glutamine help with muscle recovery, reduce fatigue and strengthen the immune system. BCAAs are especially useful in long-duration workouts, while glutamine helps maintain muscle tissue and gut health.
Creatine
Recognized for improving strength, performance in high-intensity exercises and increasing muscle mass. Creatine works by increasing energy stores (ATP) in muscles, allowing greater power during training.
Carbohydrates
Supplements like maltodextrin and dextrose provide quick energy, making them useful for long, intense workouts. Furthermore, they help to replenish muscle glycogen stores efficiently, accelerating recovery.
Caffeine
Used to improve focus, increase resistance and reduce perceived effort during exercise. Studies also indicate that caffeine can increase the mobilization of fatty acids, promoting the use of fat as an energy source.
Fish Oil (Omega-3)
Rich in essential fatty acids EPA and DHA, fish oil has anti-inflammatory properties that help with muscle recovery, reduce pain and improve cardiovascular function. For athletes, these benefits can result in shorter recovery time and better endurance.
Beta-Alanine
A supplement that increases carnosine levels in muscles, helping to buffer lactic acid and delay fatigue. It is especially useful in high-intensity, short-duration exercise.
HMB (Beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate)
A metabolite of the amino acid leucine, known to reduce muscle breakdown and accelerate recovery. HMB is particularly beneficial for beginners or during periods of intense training.
Electrolytes
Replacement of minerals such as sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium is essential to maintain hydraulic balance and prevent cramps during prolonged activities or in conditions of extreme heat.
Nitric Oxide (NO) Precursors
Supplements such as L-arginine and L-citrulline stimulate the production of nitric oxide, improving blood flow and nutrient transport to the muscles. This results in greater resistance and recovery capacity.
The Importance of Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals play a fundamental role in regulating metabolic processes and maintaining health. For athletes, ensuring adequate levels of these micronutrients is crucial:
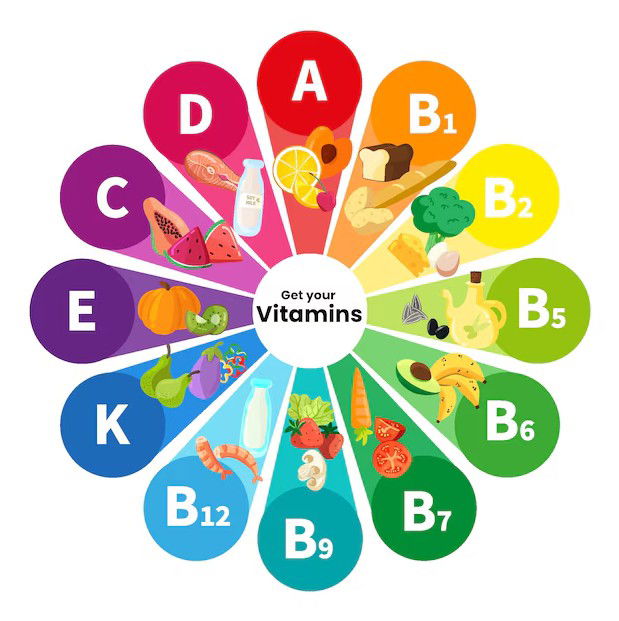
Vitamins
- Vitamin D: Important for bone health, immunity and muscle strength. It can be found in foods such as fatty fish (salmon, sardines), egg yolks and fortified products, in addition to being synthesized by the skin with exposure to the sun.
- B Complex Vitamins: Essential for energy metabolism, helping to convert carbohydrates, proteins and fats into energy. Present in lean meats, eggs, whole grains, green vegetables and legumes.
- Vitamin C: Powerful antioxidant that helps with immunity and muscle recovery. Found in citrus fruits (orange, lemon), kiwi, strawberries and vegetables such as peppers and broccoli.
- Vitamin E: Another important antioxidant, protects cells from oxidative damage. It can be found in vegetable oils, nuts, seeds and green vegetables.
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision health, immune system and cell regeneration. Sources include carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach and dairy products.
- Vitamin K: Fundamental for blood clotting and bone health. Found in green leafy vegetables, such as kale and spinach, and in vegetable oils.
Minerals
- Iron: Fundamental for transporting oxygen in the blood, preventing fatigue and improving performance. Sources include red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils and dark green vegetables.
- Calcium: Essential for bone health and muscle contraction. Found in dairy products, green vegetables like broccoli, and fortified alternatives like almond or soy milk.
- Zinc: Important for muscle recovery and immunity. Sources include beef, seafood, seeds and whole grains.
- Magnesium: Helps with muscle relaxation and energy production. It can be found in nuts, seeds, spinach, avocado and dark chocolate.
- Selenium: An antioxidant that protects against oxidative stress. Found in Brazil nuts, seafood and whole grains.
Care and Recommendations
Although supplements and vitamins offer benefits, their use should be guided by health professionals, such as nutritionists and doctors. Inadequate consumption can lead to adverse effects, such as kidney overload, nutritional imbalances or even results contrary to those desired.

Furthermore, it is important to remember again that supplements do not replace a balanced diet. They should be seen as complements for specific situations, such as increased nutritional demands or difficulties in meeting needs through diet.
Conclusion
Sports nutrition is a powerful tool for those looking to reach new levels of performance. Supplements and vitamins, when used consciously and planned, can significantly contribute to improving the athlete's performance, recovery and general health. However, balance and personalization are essential to guarantee the best results. Remember this!
Until the next article!














— Comments 0
, Reactions 1
Be the first to comment